Definition
A piston is a disc that reciprocates (up and down) inside the cylinder. At the time of the combustion process of the engine, the energy that comes out of the expanding process, transfers that energy into mechanical energy. The piston moves either due to the fuel-air mixture inside the cylinder that has been combusted, or the piston moves due to the fuel-air mixture being compressed.

Where is the piston located in the engine?
The piston is fitted in the cylinder of the engine. It is connected to the connecting rod by the piston pin and the connecting rod is connected by the crankshaft.
Piston Components or Parts:
There are a total of nine parts of the Piston assembly which are:
- Piston Rings
- Piston Head or Crown
- Piston ring grooves
- Piston skirt
- Piston pin
- Connecting rod
- Bolt
- Connecting rod bearings and
- Cap
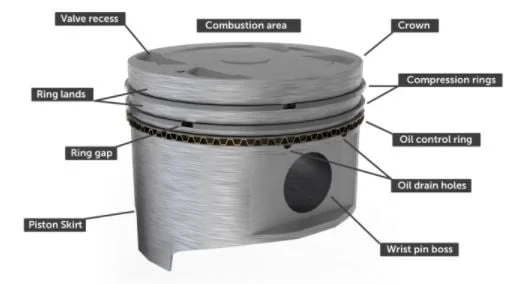
1. Piston Rings:
Piston rings are a very important component. The combustion gas that is released at the time of the engine’s combustion process should not bypass the piston, and friction is the least we can use the ring around the piston. The rings are provided by sealing between the piston and the cylinder valve.
Types of Piston rings:
There are two types of piston rings:
- Compressor Ring and
- Oil Controller Ring
Compressor Ring (Pressure Ring): The compressor ring is inserted into the top grooves of the piston. The job of the compressor ring is to transfer heat from the piston to the cylinder liner. There is also a side thrust over the piston, which causes fluctuations, the compressor ring is used to work it out.
Oil Controller ring: The oil controller ring is placed under the compressor ring. This ensures that the proper lubrication is maintained between the piston and the cylinder. And If there is access lubrication inside the cylinder, then it also works to scrap it.
2. Piston head or piston crown:
The piston crown is above the piston, due to its location, the piston crown counters very high pressure and temperature. The piston crown that is used in the timing of the confinement process, the pigment which escapes from the gas exhaust, helps it out of the engine.
3. Piston ring grooves:
It consists of grooves above the piston, which employs rings.
4. Piston skirt:
The piston skirt is the cylindrical valve of the piston. Piston skirts are made slightly rough at the time of manufacturing So that they can retain lubrication and also resist thrust.
Thrust arises due to expansion stroke. The higher the piston length, the higher will be the skirt. This will give us a better bearing surface in the piston which will not make much engine noise. But we will not increase the piston’s length too much, otherwise, its mass will increase and the inertia will also increase.
5. Piston pin:
It is also called a gudgeon pin. The pin is used to connect the piston and connecting rod. Harder steel is used as a material.
6. Connecting rod:
The connecting rod connects the piston to the crankshaft, and this functions as a liver arm and transfers motion from the piston to the crankshaft.
The connecting rod is made of cast aluminum alloy. And it is designed in such a way that it can withstand the dynamic stresses of the combustion and piston movement.
7. Bolt
The bolt is used to connect the clamp and connecting road.
8. Connecting rod bearing
The bearing is installed in two parts and together they form a complete circle. The bearing is installed between the connecting rod and the crank pin.
9. Cap
The cap is the lower part of the piston assembly. The cap is the lower half of the connecting rod which forms the house for bearing the connecting rod.
Piston Function:
The main function or work of the piston is to transfer energy by receiving the impulse that is being generated from the gas inside the cylinder and transferring the energy from the connecting rod to the crankshaft.
Another function is due to the combustion of the mixture of gas which is generating the heat, the piston works to dissipate that heat in the engine cylinder valve.
The process takes four steps in the Engine:
- Firstly in the suction stroke, it moves from TDC to BDC, then a vacuum is created in the cylinder which brings the fresh charge inside the cylinder.
- The fresh charge is compressed by the piston itself during the compressor stroke, which increases the pressure temperature of the fresh charge.
- Fuel burning in the power stroke causes the piston to be pressurized from the extra pressure causing the piston to move from TDC to BDC and transfer its power to the crankshaft via a connecting rod.
- The exhaust stroke pushes the burnt gases of the piston and the exhaust gas exits the cylinder.
It Performs some other work also:
- Helps seal the combustion chamber with the help of a ring.
- Serves as the guide work for the connecting road.
Piston Types:
- According to a piston head or Crown design: Flat, Dome type, Concave type, and Irregular head type Piston.
- According to skirt design: Solid skirt, Split skirt, Slotted, or Constant clearance piston.
- On the basis of shape and application: Slipper type, Steel inserted, Steel belted, Cam Ground, Alfinz type, and Heat type piston.
Properties of Good Piston
- It Must be strong: In a power stroke, the piston has to bear high temperature and high pressure, the temperature at the time of power stroke is from 2000 centigrade to 2500 centigrade. And pressure also means 100 times, an area foot of 1 square centimeter is equal to about 100 kg of pressure.
- It should be lightweight: Because it has to keep on moving continuously from TDC to BDC.
- Heat expansion must be reduced.
For More Press Here









